The SQL Server DateTimeOffset data type stores the date & time along with the Time Zone Offset. It is similar to both DateTime & DateTime2 data types. Except that the DateTime & DateTime2 does not store the Time Zone Offset. Also DateTime is less precise than DateTime2.
Table of Contents
What is Time Zone Offset
A Time Zone is a geographical region in which residents observe the same standard time.
A Time Zone Offset is the difference between the local time & the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).
DateTimeOffset data type stores the Time Zone Offset value along with the date & Time. But it does not store Time Zone.
Syntax
1 2 3 | datetimeoffset ([n]) |
Where n is the number of digits for the fractional part of the seconds. The value of n is from 0 to 7. n is optional and defaults to 7
Choice of n defines the fractional part of the seconds. It also determines the bytes that it needs to store. Refer to the following table
| Data type | precision & scale | Storage Size (bytes) | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| datetimeoffset *Default *Same as datetimeoffset(7) | 34,7 | 10 | 2020-12-20 17:20:12.5636531 +05:30 |
| datetimeoffset(0) | 26,0 | 8 | 2020-12-20 17:20:13 +05:30 |
| datetimeoffset(1) | 28,1 | 8 | 2020-12-20 17:20:12.6 +05:30 |
| datetimeoffset(2) | 29,2 | 8 | 2020-12-20 17:20:12.56 +05:30 |
| datetimeoffset(3) | 30.3 | 9 | 2020-12-20 17:20:12.564 +05:30 |
| datetimeoffset(4) | 31,4 | 9 | 2020-12-20 17:20:12.5637 +05:30 |
| datetimeoffset(5) | 32,5 | 10 | 2020-12-20 17:20:12.56365 +05:30 |
| datetimeoffset(6) | 33,6 | 10 | 2020-12-20 17:20:12.563653 +05:30 |
| datetimeoffset(7) | 34.7 | 10 | 2020-12-20 17:20:12.5636531 +05:30 |
Default Format
The SQL Server uses the 24 Hours format to display the time.
1 2 3 | yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss[.nnnnnnn] [{+|-}hh:mm] |
Where
yyyyrepresents the yearMMrepresents the monthddrepresents the dayhhrepresents the hour from 00 to 23mmrepresents the minute from 00 to 59ssis the second from 00 to 59nnnnnnnis the fractional part of the seconds. No of the digits comes from the column definitiontime(n). Also, note it does not use milliseconds[{+|-}hh:mm]represents the time zone offset
Time zone offset
Time zone offset is the difference between the local time to UTC Time and is specified as [+|-] hh:mm
hhis two digits that range from -14 to +14..mmis two digits that range from 00 to 59- +(plus) or -(minus) specifies whether the time zone offset is added or subtracted from the UTC time to return the local time.
The valid range of a time zone offset is -14:00 to +14:00
Range
- Date Range: 0001-01-01 to 9999-12-31
- Time Range: 00:00:00 to 23:59:59.99999
- Time zone offset range: -14:00 through +14:00
- Default Value: 1900-01-01 00:00:00 00:00
Creating DateTimeOffset Column
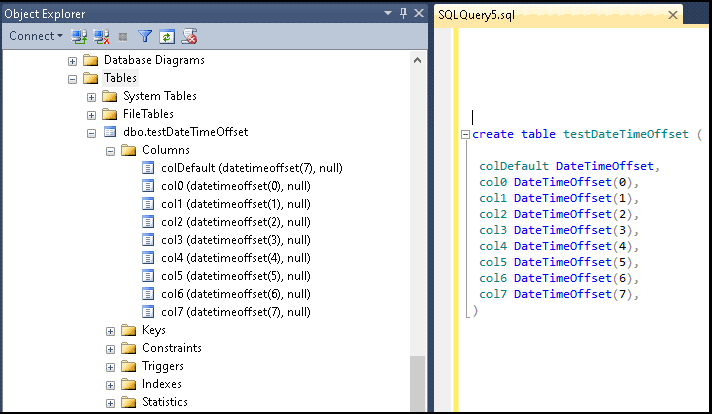
The following query shows how to create table with 8 DateTimeOffset columns, each with different n (number of digits for the fractional part of the seconds)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | create table testDateTimeOffset ( colDefault DateTimeOffset, col0 DateTimeOffset(0), col1 DateTimeOffset(1), col2 DateTimeOffset(2), col3 DateTimeOffset(3), col4 DateTimeOffset(4), col5 DateTimeOffset(5), col6 DateTimeOffset(6), col7 DateTimeOffset(7), ) |
Inserting Values
The following insert query inserts the same Date to all the DateTimeOffset columns. We use the SYSDATETIMEOFFSET() to get the current datetime with time off set.
The output shows how the different DateTimeOffset columns stores the same date value differently.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 | insert into testDateTimeOffset (colDefault, col0, col1, col2, col3, col4, col5, col6, col7 ) values (SYSDATETIMEOFFSET(), SYSDATETIMEOFFSET(), SYSDATETIMEOFFSET(), SYSDATETIMEOFFSET(), SYSDATETIMEOFFSET(), SYSDATETIMEOFFSET(), SYSDATETIMEOFFSET(), SYSDATETIMEOFFSET(), SYSDATETIMEOFFSET()) select * from testDateTimeOffset ---------------------------------- 2020-12-20 17:20:12.5636531 +05:30 -------------------------- 2020-12-20 17:20:13 +05:30 ---------------------------- 2020-12-20 17:20:12.6 +05:30 ----------------------------- 2020-12-20 17:20:12.56 +05:30 ------------------------------ 2020-12-20 17:20:12.564 +05:30 ------------------------------- 2020-12-20 17:20:12.5637 +05:30 -------------------------------- 2020-12-20 17:20:12.56365 +05:30 --------------------------------- 2020-12-20 17:20:12.563653 +05:30 ---------------------------------- 2020-12-20 17:20:12.5636531 +05:30 |
Which one to use datetime2 or datetimeoffset?
If your application is used within a single time zone, then you can use the datetime2 , which stores both date & time.
If your application spans multiple time zones , then you have two options
- One using the datetime2 and always convert the local time to UTC Time and store it
- Or Use the datetimeoffset to store the local time along with the Time zone offset