Query Parameters in Angular allow us to generate URLs with query strings. They allow us to pass optional parameters like page number, sorting & filter criteria to the component. In this tutorial, we look at how to pass the query parameters using the queryParams property of the router.navigate method or routerlink directive. We then look at how to read the parameter in the component using the ActivatedRoute Service. We also find out the difference between the Query and Route parameters and which one to use and when. Finally, we create an Angular Query Params Example application.
Table of Contents
- What are query parameters?
- Difference between Query parameters and Route parameters
- Which one to use? Route Parameters or Query Parameters?
- Adding Query Parameters
- Reading Query Parameters
- Which one to use? snapshot or observable
- queryParamsHandling
- Angular Query Params Example
- queryParamsHandling Example
- References
What are query parameters?
Query params (or Query Parameters) are key-value pairs that appear to the right of the ? in a URL. Each query parameter is separated by &.
1 2 3 | /product?page=2&filter=all |
In the above example, page=2&filter=all is the query params. It contains two query parameters. One is Page whose value is 2 and the other one is Filter whose value is all.
They are also known as query strings.
Difference between Query parameters and Route parameters
The route parameters are required and Angular Router uses them to determine the route. They are part of the route definition.
For Example, when we define the route as shown below, the id is the route parameter.
1 2 3 4 | { path: 'product', component: ProductComponent } { path: 'product/:id', component: ProductDetailComponent } |
The above route matches the following URL The angular maps the values 1 & 2 to the id field
1 2 3 4 5 6 | URL /product matches => path: 'product' /product/1 matches => path: 'product/:id' /product/2 matches => path: 'product/:id' |
The Angular Router will not navigate to the ProductDetailComponent route if the id is not provided. It will navigate to ProductComponent instead. If the product route is not defined, it will result in an error.
However, the query parameters are optional. The missing parameter does not stop angular from navigating to the route. The query parameters are added to the end of the URL Separated by Question Mark
Which one to use? Route Parameters or Query Parameters?
The best practice is to use Route Parameters to identify a specific resource or resources. For example a specific product or group of products.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | //All Products /products //specific Product /product/:id |
Use query parameters to sort, filter, paginate, etc. For example sort products based on name, rating, etc. Filter based on price, color, etc.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | //All Products sorted on rating /products?sort=rating //All Products sorted on rating with color=red /products?sort=rating&color=red //All Products sorted on rating with color=red & second page /products?sort=rating&color=red&page=2 |
The route parameters determine the route. The angular Router Module determines which component to load using them. Hence they are required.
Query Parameters are optional. Hence if you do not require the value then use the query parameter.
Adding Query Parameters
The Query parameters are not part of the route. Hence you do not define them in the routes array like route parameters. There are two ways in which you can pass a Query Parameter to Route
- Using
routerlinkdirective - Using
router.navigatemethod. - Using the router.navigateByUrl method
Using routerlink Directive in Template
We use the queryParams property of the routerlink directive to add the query parameter. We add this directive in the template file.
1 2 3 | <a [routerLink]="['product']" [queryParams]="{ page:2 }">Page 2</a> |
The router will construct the URL as
1 2 3 | /product?page=2 |
You can pass multiple Query Parameters as shown below
1 2 3 4 | <a [routerLink]="['products']" [queryParams]="{ color:'blue' , sort:'name'}">Products</a> |
The router will construct the URL as
1 2 3 | /products?color=blue&sort=name |
You can also navigate programmatically using the navigate method of the Router service as shown below
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | goTo() { this.router.navigate( ['/products'], { queryParams: { page: 2, sort:'name'} } ); } |
The above code will navigate to the following URL
1 2 3 | /products?page=2&sort=name |
You can also use the navigateByUrl method of the router. navigateByUrl expects an absolute URL, Hence we need to build our query string programmatically. Also, the navigateByUrl method does not have queryParamsHandling option.
1 2 3 | this.router.navigateByUrl('product?pageNum=2'); |
Reading Query Parameters
Reading the Query parameters is similar to reading the Router Parameter. There are two ways by which you can retrieve the query parameters.
- Subscribing to the queryParamMap or queryParams observable
- Using queryParamMap or queryParams property of the snapshot property
Both the above are part of the ActivatedRoute service. Hence we need to inject it into our component class.
Using queryParamMap observable
The queryParamMap is a Observable that returns a ParamMap of the query parameters available to the current route. We can use this to retrieve values from the query parameter. The queryParamsMap is accessible via ActivatedRoute
Hence, we need to inject the ActivatedRoute in the constructor of the component/service, where we want to read the query parameter as shown below
1 2 3 4 5 | constructor(private Activatedroute:ActivatedRoute, private router:Router){ } |
You can subscribe to the queryParamMap of the ActivatedRoute, which returns the
observable of type ParamMap.
The ParamMap object contains three methods
get method retrieves the value of the given parameter.
getAll method retrieves all parameters
has method returns true if the ParamMap contains a given parameter else false
We use the get method to read the query parameter as shown below. The following code reads the value of the pageNum query parameter.
1 2 3 4 5 6 | this.sub = this.Activatedroute.queryParamMap .subscribe(params => { this.pageNum = +params.get('pageNum')||0; }); |
Using queryParams observable
The queryParams is a Observable that returns a Params. The Params array is a list of parameter values, indexed by name.
The following code shows how to subscribe and retrieve the value of pageNum query parameter.
1 2 3 4 5 6 | this.sub = this.Activatedroute.queryParams .subscribe(params => { this.pageNum = +params.['pageNum']||0; }); |
Using snapshot.queryParamMap property
You can also read the value of the query parameter from queryParamMap using the snapshot property of the ActivatedRoute as shown below
1 2 3 4 | this.Activatedroute.snapshot .queryParamMap.get('pageNum')||0;; |
Using snapshot.queryParams property
You can also read the value of the query parameter from queryParams property of the snapshot property.
1 2 3 4 | this.Activatedroute.snapshot .queryParams['pageNum']||0;; |
Which one to use? snapshot or observable
We usually retrieve the value of the Query parameter in the ngOninit life cycle hook, when the component is initialized.
When the user navigates to the component again, and if the component is already loaded then, Angular does not create the new component but reuses the existing instance. In such circumstances, the ngOnInit method of the component is not called again.
If you are using the Snapshot to read the value of the Query parameters in ngOnInit, then you will be stuck with the values that you read when the component is loaded for the time. This is because Snapshot is not observable. Hence it will not notify you if the value changes.
By subscribing to the paramMap observable (or to the params observable), you will get a notification when the value changes. Hence you can retrieve the latest value of the parameter and update the component accordingly.
queryParamsHandling
The query parameter is lost when the user navigates to another route.
For Example, if a user navigates to the product page with the route /product?pageNum=2 and later navigates to the product detail page, angular removes the query parameter from the URL. This is the default behavior
You can change this behavior by configuring the queryParamsHandling strategy. This Configuration strategy determines how the angular router handles query parameters when the user navigates away from the current route. It has three options
- “”
- preserve
- merge
queryParamsHandling:”
This is the default option. The angular removes the query parameter from the URL when navigating to the next route.
1 2 3 4 5 | this.router.navigate(['product'], { queryParams: { pageNum: this.pageNo + 1 }, queryParamsHandling :''} ); |
1 2 3 4 | <a [routerLink]="['product']" [queryParams]="{ pageNum:2 }">Page 2</a> |
queryParamsHandling preserve
The Angular preserves or carries forwards the query parameter of the current route to the next navigation. Any query parameters of the next route are discarded
1 2 3 4 5 6 | this.router.navigate(['product'], { queryParams: { pageNum: this.pageNo + 1 }, queryParamsHandling :"preserve"} ); |
1 2 3 4 5 | <a [routerLink]="['product']" [queryParams]="{ pageNum:2 }" queryParamsHandling="preserve">Page 2</a> |
queryParamsHandling merge
The Angular merges the query parameters from the current route with that of the next route before navigating to the next route.
1 2 3 4 5 6 | this.router.navigate(['product'], { queryParams: { pageNum: this.pageNo + 1 }, queryParamsHandling :"merge"} ); |
1 2 3 4 5 | <a [routerLink]="['product']" [queryParams]="{ pageNum:2 }" queryParamsHandling="merge">Page 2</a> |
Note that preserveQueryParams is DEPRECATED
Angular Query Params Example
Let us build a small application to demonstrate the use of Query parameters. You can download the code from the Stackblitz.
The Query Params example application has two components (AppComponent & ProductComponent). The Navigation menu uses bootstrap 3 CSS.
app.component.ts
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 | import { Component } from '@angular/core'; @Component({ selector: 'my-app', template: ` <div class="container"> <nav class="navbar navbar-default"> <div class="container-fluid"> <div class="navbar-header"> <a class="navbar-brand" href="#" ><strong> {{ title }} </strong></a > </div> <ul class="nav navbar-nav"> <li><a [routerLink]="['home']">Home</a></li> <div class="navbar-form navbar-left"> <div class="form-group"> <input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="Page No" [(ngModel)]="pageNum" /> </div> </div> <li class="nav"> <a [routerLink]="['product']" [queryParams]="{ pageNum: pageNum }" >Product</a > </li> <li><a [routerLink]="['contact']">Contact us</a></li> </ul> </div> </nav> <router-outlet></router-outlet> `, }) export class AppComponent { title = 'Routing Module - Query Parameters'; pageNum = 0; } |
We have defined the pageNum variable in the component.
1 2 3 4 5 6 | export class AppComponent { title = 'Routing Module - Query Parameters'; pageNum = 0; } |
The AppComponent has the Navigation Menu. It contains the link to the product page. The link is created using the routerlink directive. The routerlink directive contains the queryParams property, where we pass the pageNum to "pageNum" variable.
1 2 3 4 | <li class="nav"><a [routerLink]="['product']" [queryParams]="{ pageNum: pageNum }">Product</a></li> |
The Angular will construct the URL as
1 2 3 | /product?pageNum=xxx |
An input box pageNum is provided so that the user can change page no.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | <div class="form-group"> <input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="Page No" [(ngModel)]="pageNum" /> </div> </div> |
product.component.ts
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 | import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core'; import { ActivatedRoute, Router } from '@angular/router'; @Component({ template: ` <h1>Product Page</h1> <p>Current Page No <strong> {{pageNo}} </strong></p> <p>snapshot Page No <strong> {{ snapshotPageNo }} </strong></p> <button (click)="nextPage()">Next Page</button> `, }) export class ProductComponent implements OnInit { pageNo = 0; snapshotPageNo = 0; constructor(private Activatedroute: ActivatedRoute, private router: Router) { } ngOnInit() { this.snapshotPageNo = +this.Activatedroute.snapshot.queryParamMap.get('pageNum') || 0; this.Activatedroute.queryParamMap.subscribe((params) => { this.pageNo = +params.get('pageNum') || 0; console.log('Query params ', this.pageNo); }); } nextPage() { this.router.navigate(['product'], { queryParams: { pageNum: this.pageNo + 1 }, }); } } |
The ProductComponent does not display any products. But it displays the query parameters received
First, we inject both ActivatedRoute and Router Service in the constructor of the ProductComponent
1 2 3 4 5 6 | constructor(private Activatedroute:ActivatedRoute, private router:Router){ } |
Next, in the ngOnInit lifecycle hook, we use the Activatedroute.snapshot method to retrieve the pageNum and update the snapshotPageNo variable.
We also subscribe to the queryParams property. We are updating our local variable pageNo with the page number obtained from the Queryparams
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | ngOnInit() { this.snapshotPageNo = this.Activatedroute.snapshot.queryParams['pageNum'] || 0; this.Activatedroute.queryParams .subscribe(params => { this.pageNum = +params['pageNum']||0; console.log('Query params ',this.pageNum) }); } |
In our template, we display both snapshotPageNo pageNo variable.
1 2 3 4 | <p>Current Page No <strong> {{pageNo}} </strong></p> <p>snapshot Page No <strong> {{ snapshotPageNo }} </strong></p> |
And a button to take us to the next page.
1 2 3 | <button (click)="nextPage()">Next Page</button> |
We also have nextPage method. It uses the router.navigate method to take us to the next page.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | nextPage() { this._router.navigate(['./'], { queryParams: { pageNum: this.pageNum + 1 }, relativeTo: this._Activatedroute } ); } |
Here we are using the router.navigate method to navigate to the next page. This actually does not change the route as we are already on the page. The angular router does not re-create the component, but since we have subscribed to the Query parameters, we will be notified of the change in page Number. The pageNum variable is updated to the new value, while the snapshotPageNo does not change
You can refer to the StackBltiz for rest of the code
Query Params Example Application in Action
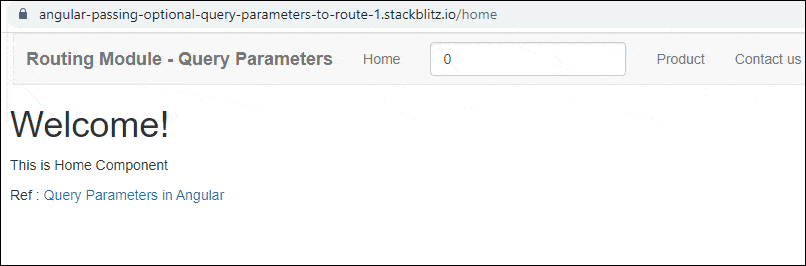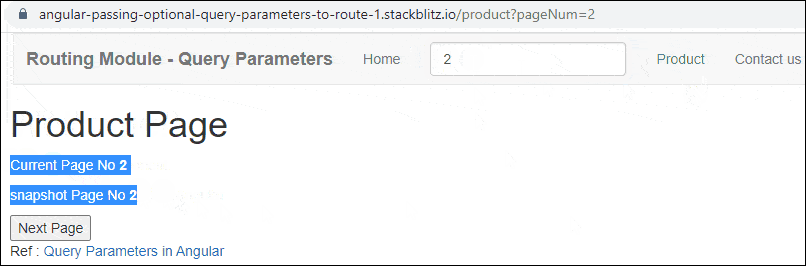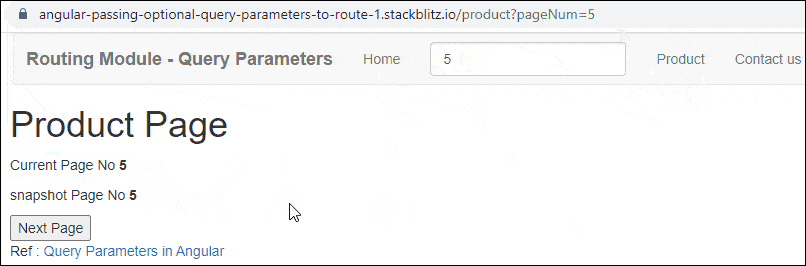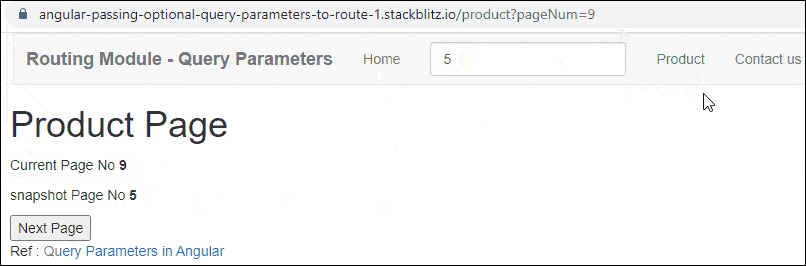
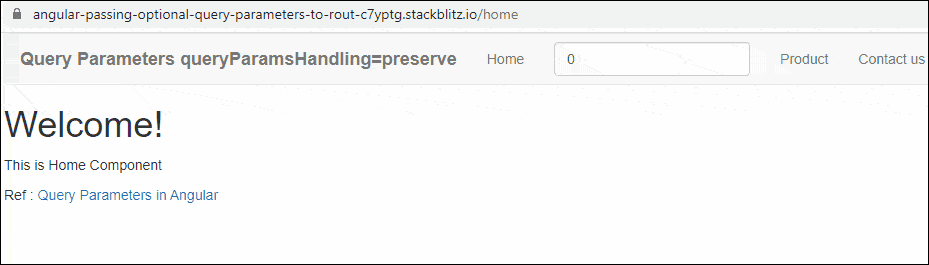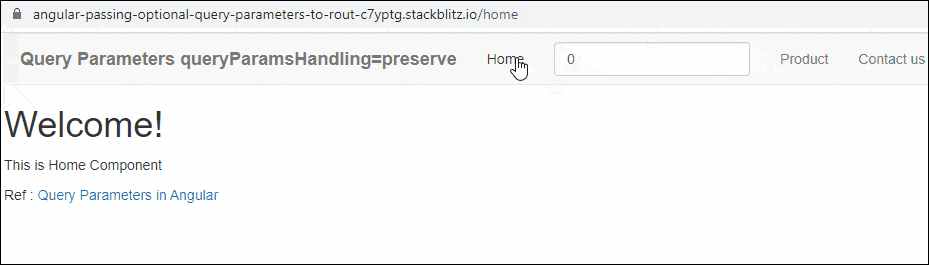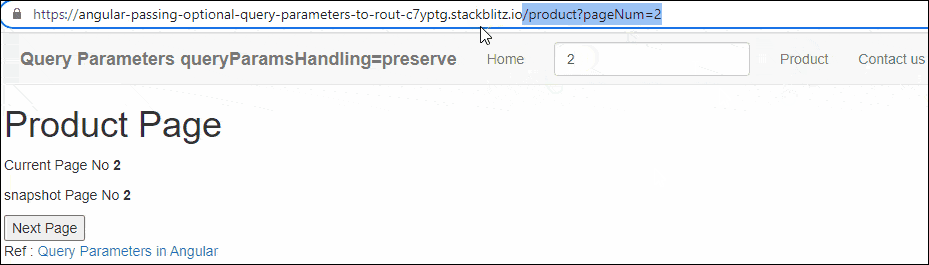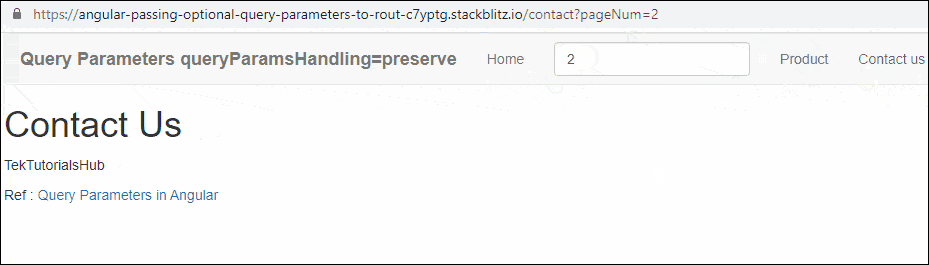
Enter the Page Number (for example 2) and click on the Product Link. You will navigate to the Product Page with the URL /product/pageNum=2. The Product Component reads the pageNum from the Activatedroute service. You will observe that the snapshot Page Number is the same as the page number obtained from the observable
Click on Next Page will change the URL and Page No. But Angular will not reload the Component because the component is already loaded. Hence the snapshot Page Number will remain the same.
queryParamsHandling Example
Open the app.component.ts and add the queryParamsHandling=’preserve’ to the contact page routerLink
1 2 3 4 5 | <a [routerLink]="['contact']" queryParamsHandling='preserve' >Contact us</a> |
Now navigate to the Product Page and then to the Contact us page. You will see that the URL will retain the query strings.
References
Read More
- Angular Tutorial
- Routing and Navigation in Angular
- Location Strategies in Angular Router
- Passing Parameters to Route
- Child Routes / Nested Routes
- Passing Optional (Query) Parameters to a route
- Navigation between Routes
- Angular Route Guards
- CanActivate Guard
- CanActivateChild Guard
- CanDeactivate Guard
- Angular Resolve Guard
- Angular Pass data to route
- RouterLinkActive
- Router Events



Not tested yet, will it work if the user directly copy an url with query params and inject it in the browser ?
thank you very much you explained really nice
I really wanna thank you for your straightforward explanation, great.
Thank you so much for explaining it.
how can we pass the query params to external application??
I want to pass jwt and user id from angular to the php page so how can i achieve this ?
you have to pass these information through HTTP request header(jwt token) and body(user info) section and not through query param.
Thanks