Angular allows us to pass data through the route. The route data can be either static or dynamic. The static data use the Angular route data property, where you can store arbitrary data associated with that specific route. To pass dynamic data (or an object), we can use the history state object. The Routed Component can then retrieve the dynamic data from the history state object.
Table of Contents
Various ways of passing route data
Angular components can share data in many ways. The parent can communicate with their child using @Input directive. A child can pass data to the Parent using the @Output & EventEmitter. The parent can use the @ViewChild to access the child component. In case of components are unrelated then we can use the Angular Services to Share data between them.
We can also share data between components using the route. Angular can pass data through the route in several ways.
- Using Route Parameter
- The Query Parameters or Query Strings
- Using URL Fragment
- Static data using the data property
- Dynamic data using the state object
In this article, we look at how to pass static or dynamic data using the Route. i.e. items 4 & 5 in the above list.
Passing static data to a route
We can configure the static data at the time of defining the route. This is done by using the Angular route data property of the route. The route data property can contain an array of arbitrary string key-value pairs. You can use the static data to store items such as page titles, breadcrumb text, and other read-only, static data
For Example, consider the following route with the data property set
1 2 3 | { path: 'static', component: StaticComponent, data :{ id:'1', name:"Angular"}}, |
The Angular Router will pass the { id:'1', name:"Angular"} when the StaticComponent is rendered. The data value will be located in the data property of the ActivatedRoute service
We can then read the data by subscribing to the activatedroute.data property as shown below
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | ngOnInit() { this.activatedroute.data.subscribe(data => { this.product=data; }) } |
Passing Dynamic data to a Route
The option to pass the dynamic data or a user-defined object was added in Angular Version 7.2 using the state object. The state object is stored in History API
Providing the State value
The state can be provided in two ways
Using routerLink directive
1 2 3 | <a [routerLink]="['dynamic']" [state]="{ id:1 , name:'Angular'}">Dynamic Data</a> |
Using navigateByUrl
1 2 3 | this.router.navigateByUrl('/dynamic', { state: { id:1 , name:'Angular' } }); |
navigationId is a number, which is incremented every time we navigate from one route to another. Angular uses it to identify every navigation. The Router will add a navigationId property to the state object. Because of that, we can only assign an object to the State object.
Hence we cannot store primitive types like strings or numbers etc. For example, the following code results in an error because we are passing a string.
1 2 3 | this.router.navigateByUrl('/dynamic', { state: 'Angular' }); |
You can only assign an object to the state object. The following code is ok.
1 2 3 | this.router.navigateByUrl('/dynamic', { state: {name: 'Angular' } }); |
Accessing the state value
The state can be accessed by using the getCurrentNavigation method of the router (works only in the constructor)
1 2 3 | this.router.getCurrentNavigation().extras.state |
Or use the history.state in the ngOnInit.
1 2 3 | console.log(history.state) |
or use the getState method of the Location Service. This method is available in Angular 8+
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | import { Location } from '@angular/common'; export class SomeComponent { products:Product[]; constructor(private location:Location){ } ngOnInit() { console.log(this.location.getState()); } } |
Note that you will lose the dynamic data if the page is refreshed.
Passing Data to the Routes Example
Let us build a simple project to demonstrate how to pass data to the route
Passing static data example
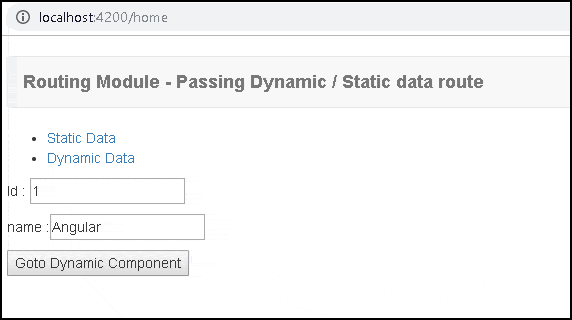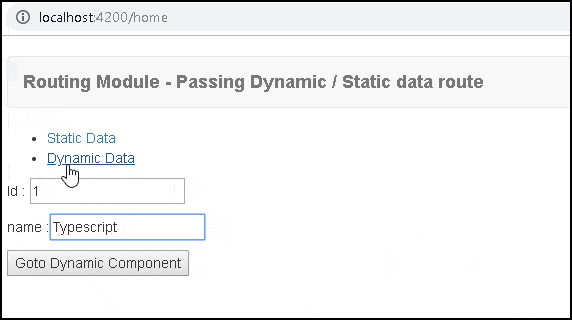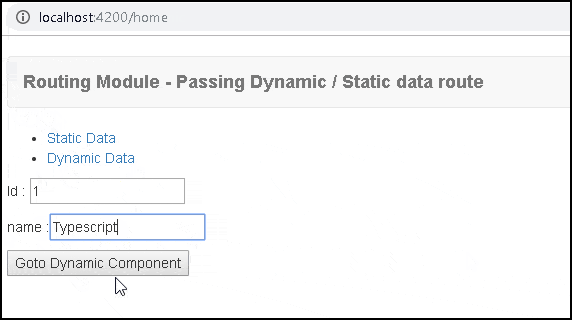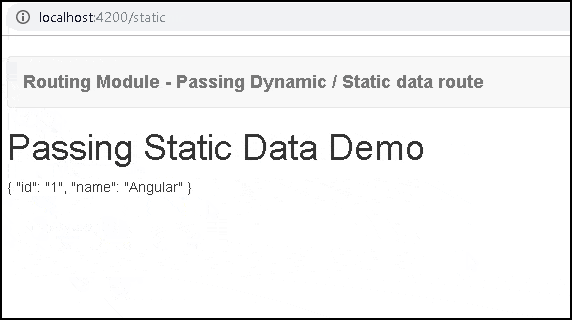
static.component.ts
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | import {Component, OnInit} from '@angular/core'; import { ActivatedRoute } from '@angular/router'; @Component({ template: `<h1>Passing Static Data Demo</h1> {{product | json}}` }) export class StaticComponent implements OnInit { product:any; constructor(private activatedroute:ActivatedRoute) { } ngOnInit() { this.activatedroute.data.subscribe(data => { this.product=data; }) } } |
The static component gets the static data configured in the route. It subscribes the activatedroute.data property to get the product data as shown above.
Passing dynamic data (or object) example
dynamic.component.ts
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | import {Component, OnInit, ChangeDetectorRef} from '@angular/core'; import { ActivatedRoute, Router, NavigationStart } from '@angular/router'; import { map, filter} from 'rxjs/operators'; import { Observable} from 'rxjs/observable'; @Component({ template: `<H1>Passing Dynamic Data Demo</H1> {{ product | json }}` }) export class DynamicComponent implements OnInit { product; constructor(private router:Router, private activatedRoute:ActivatedRoute) { console.log(this.router.getCurrentNavigation().extras.state); } ngOnInit() { //console.log(history.state); this.product=history.state; } } |
The Dynamic Component gets dynamic data. We use the history.state to access the product data. Alternatively, we can use the this.router.getCurrentNavigation().extras.state to achieve the same. Please remember getCurrentNavigation only works in the constructor. It will return null if used elsewhere.
home.component.ts
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | import { Component } from '@angular/core'; import { ActivatedRoute, Router } from '@angular/router'; @Component({ template: ` <ul> <li><a [routerLink]="['/static']">Static Data</a></li> <li><a [routerLink]="['/dynamic']" [state]=product>Dynamic Data</a></li> </ul> <p>Id : <input type="text" [(ngModel)]="product.id" > </p> <p>name :<input type="text" [(ngModel)]="product.name" > </p> <button (click)="gotoDynamic()" >Goto Dynamic Component</button>` }) export class HomeComponent { public product = { id:'1', name:"Angular"}; constructor(private router : Router) { } gotoDynamic() { //this.router.navigateByUrl('/dynamic', { state: { id:1 , name:'Angular' } }); this.router.navigateByUrl('/dynamic', { state: this.product }); } } |
In HomeComponent, we have used routerLink & navigateByUrl to pass the data to the dynamic component. You can also use the form fields to change the data, before passing it to the dynamic route.
app.routes.ts
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | import { Routes } from '@angular/router'; import { StaticComponent} from './static.component' import { DynamicComponent } from './dynamic.component'; import { HomeComponent } from './home.component'; export const appRoutes: Routes = [ { path: 'home', component: HomeComponent }, { path: 'static', component: StaticComponent, data :{ id:'1', name:"Angular"}}, { path: 'dynamic', component: DynamicComponent }, { path: '', redirectTo: 'home', pathMatch: 'full' } ]; |
Here the static data is set for StaticComponent using the data property.
app.component.ts
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | import { Component } from '@angular/core'; @Component({ selector: 'app-root', template: `<div class="container"> <nav class="navbar navbar-default"> <div class="container-fluid"> <div class="navbar-header"> <a class="navbar-brand" [routerLink]="['/']"><strong> {{title}} </strong></a> </div> </div> </nav> <router-outlet></router-outlet> </div>` }) export class AppComponent { title = 'Routing Module - Passing Dynamic / Static data route'; } |
app.module.ts
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 | import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser'; import { NgModule } from '@angular/core'; import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms'; import { HttpModule } from '@angular/http'; import { RouterModule } from '@angular/router'; import { AppComponent } from './app.component'; import { StaticComponent} from './static.component' import { appRoutes } from './app.routes'; import { DynamicComponent } from './dynamic.component'; import { HomeComponent } from './home.component'; @NgModule({ declarations: [ AppComponent,StaticComponent,DynamicComponent,HomeComponent ], imports: [ BrowserModule, FormsModule, HttpModule, RouterModule.forRoot(appRoutes) ], providers: [], bootstrap: [AppComponent] }) export class AppModule { } |



{ navigationId : 12 ,
search : “data” }
i got this in using of history.state method for read data
so my question is what is “navigationId”
navigationId is a number, which is incremented every time we navigate from one route to another. Angular uses it to identify every navigation. The Router will add a navigationId property to the state object
Updated the article
I have a question. how to route to external link. By clicking on the route, it should open a website for example http://www.google.com or any website?
Excellent!, simple and quickly just someone needed, just remeber everytime you subscribe in a component always unsubscribe on ngOnDestroy cycle event of that component.
Unsubscribing is not mandatory when using activatedroute and router. see official docs for reference https://angular.io/guide/router-tutorial-toh#observable-parammap-and-component-reuse
Awesome! So far, this is exactly what I needed. Thank you.
When passing dynamically, the data gets sent to the component you navigate to but refreshing the page results in an error
same
i am try to do this in angular 11 but not work.
data is empty object.
how solve this.
Should work in Angular 11
Check the stackblitz
https://stackblitz.com/edit/angular-pass-data-to-route-1
routing overwrites passed queryParams described in url and redirects it to the same page without by cutting queryParams . how is possible to configure routing to accept queryparams and keep it during navigation?
from this http://localhost:xxxx/#/x/type=a&value=somevalue
it overwrites and becomes
http://localhost:xxxx/#/x/type=a
is this work on browser refresh?
Static data is defined on route and will work on a refresh
Dynamic data will not work