The Angular Resolve Guard or Angular Resolvers allow us to load data before we navigate to a Route. This article will show you what Angular Resolve guard is and how to use it in an Angular App.
Table of Contents
Angular Resolve Guard
The Angular renders the Angular Component when we navigate to a route. The component will then send an HTTP request to the back-end server to fetch data to display it to the user. We generally do this in the ngOnInit Life cycle hook
The Problem with the above approach is that the user will see an empty component. The component shows the data after the arrival of the data. One way to solve this problem is to show some loading indicators.
Another way to solve this is to make use of the Resolve Guard. The Resolve Guard pre-fetches the data before navigating to the route. Hence the component is rendered along with the data.
How to Use Resolve Guard
First, we need to create a Angular Service, which implements the Resolve Interface
The service must implement the resolve method. A resolve method must return either an Observable<any>, Promise<any>, or just data. The interface signature of the Resolve interface is shown below.
1 2 3 4 5 | interface Resolve<T> { resolve(route: ActivatedRouteSnapshot, state: RouterStateSnapshot): Observable<T> | Promise<T> | T } |
Inside the Resolve method, we will get the access to the ActivatedRouteSnapshot & RouterStateSnapshot, which can be used to get the values of router parameter, query parameters etc.
The following is the simple example of a Angular Resolver.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | import { Injectable } from '@angular/core'; import { Resolve, ActivatedRouteSnapshot,RouterStateSnapshot } from '@angular/router'; import { ProductService } from './product.service'; import { Observable, of } from 'rxjs'; @Injectable() export class ProductListResolveService implements Resolve<any>{ constructor(private _router:Router , private productService:ProductService ) { } resolve(route: ActivatedRouteSnapshot, state: RouterStateSnapshot): Observable<any> { return this.productService.getProducts(); } } |
First, we import the Resolve from the @angular/router module.
We can make use of Angular Dependency Injection to inject the required services in the constructor.
The resolve method must return either an Observable<any>, Promise<any>, or just data. In the example above, we are invoking the getProducts method of method of the productService, which returns an observable.
The router does not create the instance of the resolver. The job falls on the Angular dependency injection. Hence, we need it to register it in the Providers array of root module.
1 2 3 | providers: [ProductListResolveGuardService] |
Once the resolver is created, we need to update the route definition and add the resolve property, as shown below.
1 2 3 | { path: 'product', component: ProductComponent, resolve: {products: ProductListResolveService} }, |
The resolve property is a JavaScript object of key-value pair of resolvers. The key is a user-defined variable. The value must be a resolver service.
In the example above, products are the key, and ProductListResolveService is the resolver. The return value of the ProductListResolveService is assigned to the key, i.e., products, and made available to the component via route data
When the user navigates to the route product, the angular looks for the route's resolve property. The angular calls the resolve method for each key-value pair of resolvers. If the return value of the resolver is observable or a promise, the router will wait for that to complete. The returned value is assigned to the key products and added to the route data collection.
The component can just read the products from the route data from the ActivatedRoute as shown below.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | constructor(private route: ActivatedRoute){ } ngOnInit() { this.products=this.route.snapshot.data['products']; } |
Remember Resolve runs after all other guards are executed
If you return null from the resolver, the router will cancel the navigation
If the error is generated, then the router will cancel the navigation.
Multiple Resolvers
You can define more than one resolver
1 2 3 4 | { path: 'product', component: ProductComponent, resolve: {products: ProductListResolveService, , data:SomeOtherResolverService} } |
Resolve Guard Example
Let us build a simple app to demonstrate the use of Resolve guard.
Product Service
The following is the simple ProductService, which retrieves the hard coded products.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 | import {Product} from './Product' import { of, Observable, throwError} from 'rxjs'; import { delay, map } from 'rxjs/internal/operators'; export class ProductService{ products: Product[]; public constructor() { this.products=[ new Product(1,'Memory Card',500), new Product(2,'Pen Drive',750), new Product(3,'Power Bank',100), new Product(4,'Computer',100), new Product(5,'Laptop',100), new Product(6,'Printer',100), ] } //Return Products List with a delay public getProducts(): Observable<Product[]> { return of(this.products).pipe(delay(1500)) ; } // Returning Error // This wil stop the route from getting Activated //public getProducts(): Observable<Product[]> { // return of(this.products).pipe(delay(1500), map( data => { // throw throwError("errors occurred") ; // })) //} public getProduct(id): Observable<Product> { var Product= this.products.find(i => i.productID==id) return of(Product).pipe(delay(1500)) ; } } |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | export class Product { constructor(productID:number, name: string , price:number) { this.productID=productID; this.name=name; this.price=price; } productID:number ; name: string ; price:number; } |
The getProducts() method returns the Observable of products using the RxJS operator of. We have included a delay of 1500 ms.
Similarly, the getProduct(id) returns the observable of Product after a delay of 1500 ms.
Product Component without resolver
Next, let us build two components to display the list of Products. The first component Product1Component does not use a resolver. The second component Product1Component makes use of the resolver.
This component, subscribes to the getProducts() method of the ProductService to get the list of Products
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core'; import { ProductService } from './product.service'; import { Product } from './product'; import { ActivatedRoute } from '@angular/router'; @Component({ templateUrl: './product1.component.html', }) export class Product1Component { public products:Product[]; constructor(private route: ActivatedRoute,private productService:ProductService){ } ngOnInit() { this.productService.getProducts().subscribe(data => { this.products=data; }); } } |
Resolve Guard
The ProductListResolverService service implements the Resolve Interface. It just returns the productService.getProducts().
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | import { Injectable } from '@angular/core'; import { Resolve, ActivatedRouteSnapshot,RouterStateSnapshot } from '@angular/router'; import { ProductService } from './product.service'; import { Observable, of } from 'rxjs'; import { Product } from './Product'; @Injectable() export class ProductListResolverService implements Resolve<Product>{ constructor(private productService:ProductService ) { } resolve(route: ActivatedRouteSnapshot, state: RouterStateSnapshot): Observable<any> { console.log("ProductListResover is called"); return this.productService.getProducts(); } } |
Product Component with resolver
The following is the Product2Component does not use the ProductService, but gets the product list from the Route data.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core'; import { ProductService } from './product.service'; import { Product } from './product'; import { ActivatedRoute } from '@angular/router'; @Component({ templateUrl: './product2.component.html', }) export class Product2Component { public products:Product[]; constructor(private route: ActivatedRoute,private productService:ProductService){ } ngOnInit() { this.products=this.route.snapshot.data['products']; } } |
In the app.routing.module, we need to add the resolve guard in the route definition
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | export const appRoutes: Routes = [ { path: 'home', component: HomeComponent }, { path: 'contact', component: ContactComponent }, { path: 'product1', component: Product1Component }, { path: 'product2', component: Product2Component, resolve: {products: ProductListResolverService} } ] |
The register the ProductListResolverService in Providers array in AppModule
1 2 3 | providers: [ProductService,ProductListResolverService], |
Finally, run the app
As you click on the Product1 link, you will see that the component gets loaded, but the data appears after a delay.
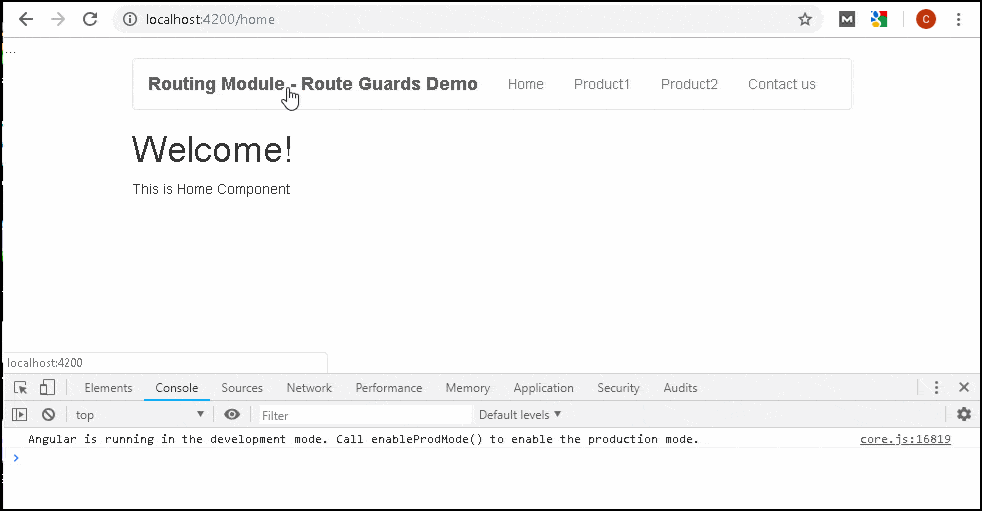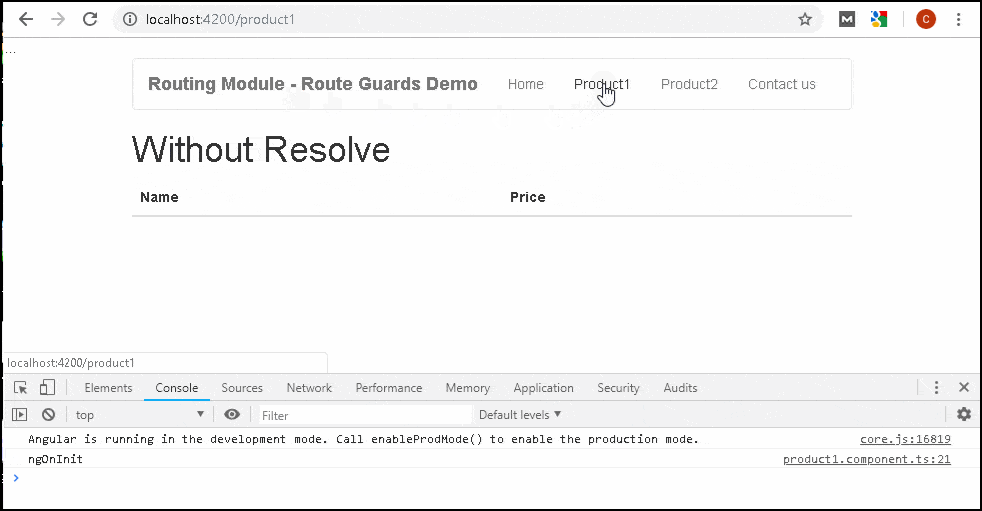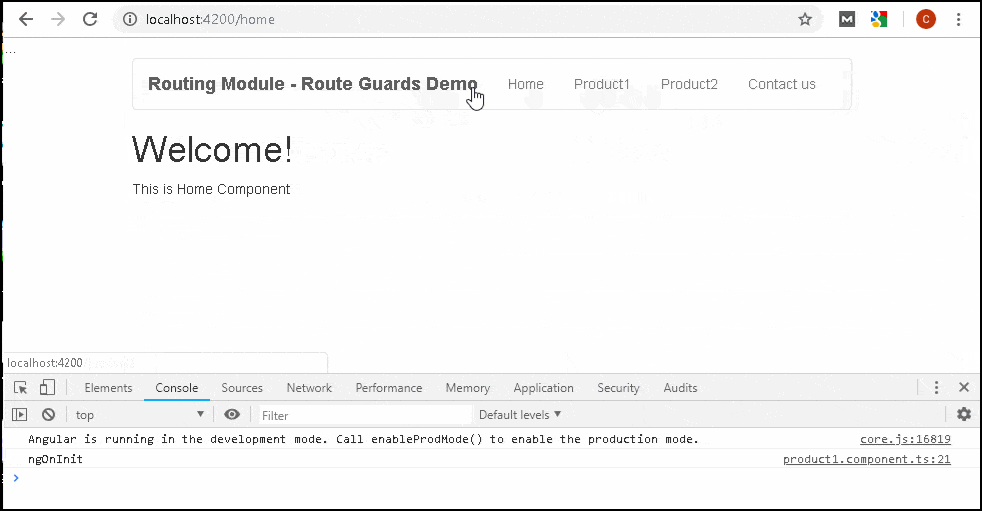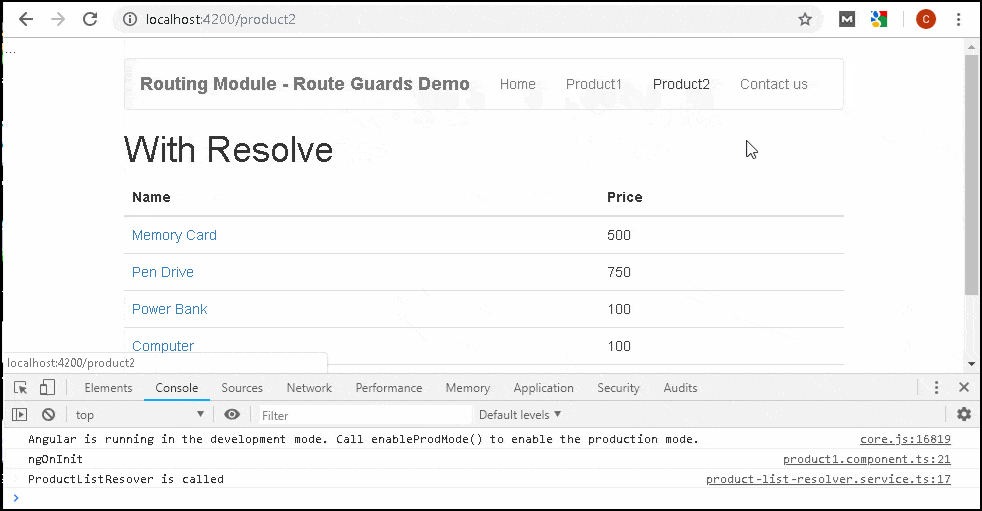
While you click on Product2 the component itself appears after some delay. That is because it waits for the resolver to finish. The Component renders along with the data.
ProductDetail Component
We can continue and create Product2DetailComponent and create a resolver, which if product not found redirects us to the Product2Component.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 | import { Injectable } from '@angular/core'; import { Router, Resolve, ActivatedRouteSnapshot,RouterStateSnapshot } from '@angular/router'; import { ProductService } from './product.service'; import { Observable, of } from 'rxjs'; import { catchError, map } from 'rxjs/internal/operators'; import { Product } from './Product'; @Injectable() export class ProductResolverService implements Resolve<any>{ constructor(private router:Router , private productService:ProductService ) { } resolve(route: ActivatedRouteSnapshot, state: RouterStateSnapshot): any { let id = route.paramMap.get('id'); console.log("ProductResolverService called with "+id); return this.productService.getProduct(id) .pipe(map( data => { if (data) { console.log(data); return data; } else { console.log('redirecting'); this.router.navigate(['/product2']); return null } })) } } |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | import { Component } from '@angular/core'; import { ActivatedRoute } from '@angular/router'; import { Product } from './product'; @Component({ templateUrl: './product2-detail.component.html', }) export class Product2DetailComponent { product:Product; constructor(private _Activatedroute:ActivatedRoute){ this.product=this._Activatedroute.snapshot.data['product']; } } |
In the resolver service, we check to see if the product exists, if not we redirect the use the product list page and return null.
Complete Example
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 | import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser'; import { NgModule, ErrorHandler } from '@angular/core'; import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms'; import { HttpModule } from '@angular/http'; import { RouterModule } from '@angular/router'; import { AppComponent } from './app.component'; import { HomeComponent} from './home.component' import { ContactComponent} from './contact.component' import { ProductService } from './product.service'; import { ProductListResolverService } from './product-list-resolver.service'; import { ProductResolverService } from './product-resolver.service'; import { AppRoutingModule } from './app-routing.module'; import { Product1Component } from './product1.component'; import { Product1DetailComponent} from './product1-detail.component' import { Product2Component } from './product2.component'; import { Product2DetailComponent } from './product2-detail.component'; @NgModule({ declarations: [ AppComponent,HomeComponent,ContactComponent,Product1Component, Product2Component,Product1DetailComponent, Product2DetailComponent ], imports: [ BrowserModule, FormsModule, HttpModule, RouterModule, AppRoutingModule ], providers: [ProductService,ProductListResolverService,ProductResolverService,], bootstrap: [AppComponent] }) export class AppModule { } |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | import { Component } from '@angular/core'; @Component({ selector: 'app-root', templateUrl: './app.component.html', styleUrls: ['./app.component.css'] }) export class AppComponent { title = 'Routing Module - Route Guards Demo'; } |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | <div class="container"> <nav class="navbar navbar-default"> <div class="container-fluid"> <div class="navbar-header"> <a class="navbar-brand" [routerLink]="['/']"><strong> {{title}} </strong></a> </div> <ul class="nav navbar-nav"> <li><a [routerLink]="['home']">Home</a></li> <li><a [routerLink]="['product1']">Product1</a></li> <li><a [routerLink]="['product2']">Product2</a></li> <li><a [routerLink]="['contact']">Contact us</a></li> </ul> </div> </nav> <router-outlet></router-outlet> </div> |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 | import { NgModule} from '@angular/core'; import { Routes,RouterModule } from '@angular/router'; import { HomeComponent} from './home.component' import { ContactComponent} from './contact.component' import { Product1Component} from './product1.component' import { Product2Component} from './product2.component' import { Product1DetailComponent} from './product1-detail.component' import { ProductListResolverService } from './product-list-resolver.service'; import { Product2DetailComponent } from './product2-detail.component'; import { ProductResolverService } from './product-resolver.service'; export const appRoutes: Routes = [ { path: 'home', component: HomeComponent }, { path: 'contact', component: ContactComponent }, { path: 'product1', component: Product1Component }, { path: 'product2', component: Product2Component, resolve: {products: ProductListResolverService} }, { path: 'product1/:id', component: Product1DetailComponent }, { path: 'product2/:id', component: Product2DetailComponent, resolve:{product:ProductResolverService} }, { path: '', redirectTo: 'home', pathMatch: 'full' }, ]; @NgModule({ declarations: [ ], imports: [ RouterModule.forRoot(appRoutes) ], providers: [], bootstrap: [] }) export class AppRoutingModule { } |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | import {Component} from '@angular/core'; @Component({ template: `<h1>Contact Us</h1> <p>TekTutorialsHub </p> ` }) export class ContactComponent { } |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | import {Component} from '@angular/core'; @Component({ template: `<h1>Welcome!</h1> <p>This is Home Component </p> ` }) export class HomeComponent { } |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | export class Product { constructor(productID:number, name: string , price:number) { this.productID=productID; this.name=name; this.price=price; } productID:number ; name: string ; price:number; } |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 | import {Product} from './Product' import { of, Observable, throwError} from 'rxjs'; import { delay, map } from 'rxjs/internal/operators'; export class ProductService{ products: Product[]; public constructor() { this.products=[ new Product(1,'Memory Card',500), new Product(2,'Pen Drive',750), new Product(3,'Power Bank',100), new Product(4,'Computer',100), new Product(5,'Laptop',100), new Product(6,'Printer',100), ] } //Return Products List with a delay public getProducts(): Observable<Product[]> { return of(this.products).pipe(delay(1500)) ; } // Returning Error // This wil stop the route from getting Activated //public getProducts(): Observable<any> { // return of(this.products).pipe(delay(3000), map( data => { // throw throwError("errors occurred") ; // })) //} public getProduct(id): Observable<Product> { var Product= this.products.find(i => i.productID==id) return of(Product).pipe(delay(1500)) ; } } |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | import { Injectable } from '@angular/core'; import { Router, Resolve, ActivatedRouteSnapshot,RouterStateSnapshot } from '@angular/router'; import { ProductService } from './product.service'; import { Observable, of } from 'rxjs'; @Injectable() export class ProductListResolverService implements Resolve<any>{ constructor(private productService:ProductService ) { } resolve(route: ActivatedRouteSnapshot, state: RouterStateSnapshot): Observable<any> { console.log("ProductListResover is called"); return this.productService.getProducts(); } } |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 | import { Injectable } from '@angular/core'; import { Router, Resolve, ActivatedRouteSnapshot,RouterStateSnapshot } from '@angular/router'; import { ProductService } from './product.service'; import { Observable, of } from 'rxjs'; import { catchError, map } from 'rxjs/internal/operators'; import { Product } from './Product'; @Injectable() export class ProductResolverService implements Resolve<any>{ constructor(private router:Router , private productService:ProductService ) { } resolve1(route: ActivatedRouteSnapshot, state: RouterStateSnapshot): Observable<any> { console.log("ProductResolverService called"); let id = route.paramMap.get('id'); return this.productService.getProduct(id); } resolve(route: ActivatedRouteSnapshot, state: RouterStateSnapshot): any { let id = route.paramMap.get('id'); console.log("ProductResolverService called with "+id); return this.productService.getProduct(id) .pipe(map( data => { if (data) { console.log(data); return data; } else { console.log('redirecting'); this.router.navigate(['/product2']); return null } })) } } |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core'; import { ProductService } from './product.service'; import { Product } from './product'; import { ActivatedRoute } from '@angular/router'; @Component({ templateUrl: './product1.component.html', }) export class Product1Component { public products:Product[]; constructor(private route: ActivatedRoute,private productService:ProductService){ } ngOnInit() { console.log('ngOnInit'); this.productService.getProducts().subscribe(data => { this.products=data; }); } } |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | <h1> Without Resolve</h1> <div class='table-responsive'> <table class='table'> <thead> <tr> <th>Name</th> <th>Price</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr *ngFor="let product of products;"> <td><a [routerLink]="['/product1',product.productID]">{{product.name}} </a> </td> <td>{{product.price}}</td> </tr> </tbody> </table> </div> |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | import { Component } from '@angular/core'; import { Router,ActivatedRoute } from '@angular/router'; import { ProductService } from './product.service'; import { Product } from './product'; @Component({ templateUrl: './product1-detail.component.html', }) export class Product1DetailComponent { product:Product; constructor(private _Activatedroute:ActivatedRoute, private _router:Router, private _productService:ProductService){ let id=this._Activatedroute.snapshot.params['id']; console.log(id); this._productService.getProduct(id) .subscribe( data => { this.product=data console.log(this.product); }) } } |
1 2 3 4 5 6 | <h1>Product Details Page [Without resolve]</h1> Product : {{ product?.name}} <br> Price : {{product?.price}} |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core'; import { ProductService } from './product.service'; import { Product } from './product'; import { ActivatedRoute } from '@angular/router'; @Component({ templateUrl: './product2.component.html', }) export class Product2Component { public products:Product[]; constructor(private route: ActivatedRoute,private productService:ProductService){ } ngOnInit() { this.products=this.route.snapshot.data['products']; } } |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | <h1> With Resolve</h1> <div class='table-responsive'> <table class='table'> <thead> <tr> <th>Name</th> <th>Price</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr *ngFor="let product of products;"> <td><a [routerLink]="['/product2',product.productID]">{{product.name}} </a> </td> <td>{{product.price}}</td> </tr> </tbody> </table> </div> |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | import { Component } from '@angular/core'; import { ActivatedRoute } from '@angular/router'; import { Product } from './product'; @Component({ templateUrl: './product2-detail.component.html', }) export class Product2DetailComponent { product:Product; constructor(private _Activatedroute:ActivatedRoute){ this.product=this._Activatedroute.snapshot.data['product']; } } |
1 2 3 4 5 6 | <h1>Product Details Page [With resolve]</h1> Product : {{ product?.name}} <br> Price : {{product?.price}} |



Wow what a wonderful explaination, it’s really good for who have to understand deep information about how to use and how Resolver is working in angular
Thanks a lot who written this article 🙏
Could it be that one pitfall of using resolvers is that it impacts the UX by not giving feedback while the data is being loaded? as you are not rendering the component while the resolver is active?
Totally agree with you. User might think nothing is happening and they might make duplicate clicks or just move away from app!
hi,
you have a source code or github the all of exemple guards
thank you
Very neatly explained, very much clear. Thank you.