Environment Variables are one of the sources from which ASP.NET Core reads the configuration values. In this tutorial, let us learn how to set Environment Variables in Windows, Mac, Linux, IIS Server, Visual Studio, Visual Studio Code & dotnet run. We also learn how to read them in ASP.NET core.
Table of Contents
Setting the Environment Variables
How we set environment variable depends on the OS
Windows
There are three ways in which you can set the environment variable in Windows
- Command-line utility
- PowerShell
- Windows GUI Tool
Command Line Utility
Using the set command
use the set command to temporarily set the environment variable.
1 2 3 | D:\>set Key="Key from environment" |
- It will affect the current shell
- change is immediate
- change is lost, when you close the shell
- will not affect any other shell
Using the setx command
The following command sets the variable for the current logged in user and the change is permanent.
1 2 3 4 5 | D:\>setx Key "Key from environment" SUCCESS: Specified value was saved. |
But the changes are reflected only if you close the current window and open another window.
setxcreates the environment value permanently.- The change will not affect the current shell or the shells that are already running.
- You need to open a new shell for the changes to become available.
- Only affects the current logged in user.
- To make the variable available to all users (machine-wide) use the
setxwith/mflag
The /m flag saves the changes globally (machine wise). Hence it will be available to all the users
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | D:\>setx Key "Key from environment" /m SUCCESS: Specified value was saved. D:\> |
PowerShell
PowerShell is the another way to change the Environment Variable
For temporary changes use the $Env. it is similar to the set command.
1 2 3 | $Env:Key = "Key from environment" |
for Permanent changes use the [Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable. Use the third argument to set the variable User wise or machine wise.
1 2 3 4 | [Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("Key", "Key from environment", "User") [Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("Key", "Key from environment", "Machine") |
Windows GUI tools
You can update the environment variable using the Windows GUI tools. Search for edit environment variable and click on the option as shown below.
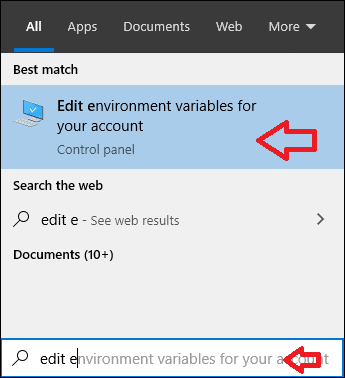
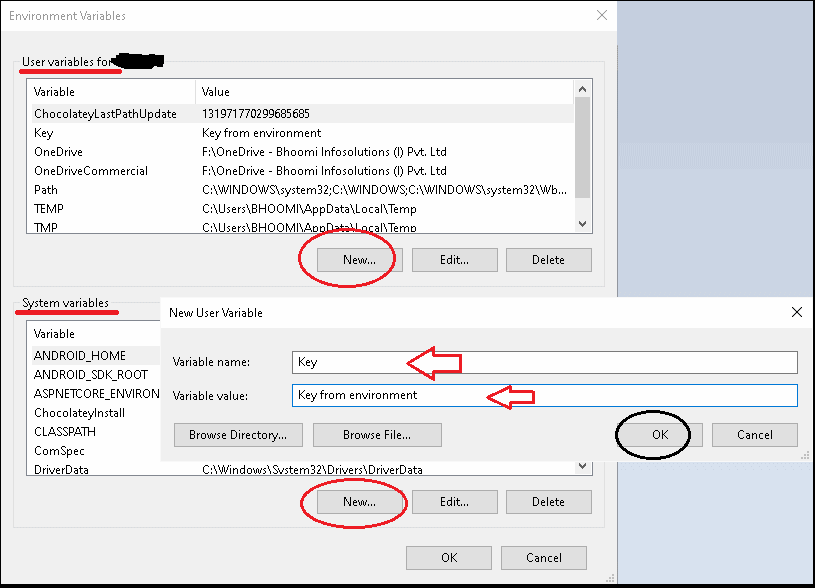
This will open the Environment variables window, where you can use the New button to add a new environment variable.
Add it to the User Variables if you want to set the variable only for the current logged in user or use the System variables for all the logged-in users.
Linux/ Mac
Use the export to temporarily set the Environment variable.
1 2 3 | export Key='Key from linux environment' |
To check if it correctly set use the echo command
1 2 3 | echo $KEY |
Remove the variable using the unset command
1 2 3 | unset Key |
To save the variable permanently you need to consider the shell that you are using. The most used shell is the bash shell. But the latest version of Mac uses the Zsh Shell.
bash shell
- login shell will load
/etc/profile,~/.bash_profile,~/.bash_login,~/.profilein the order - non-login interactive shell will load
~/.bashrc - non-login non-interactive shell will load the configuration specified in the environment variable
$BASH_ENV
Open the shell file in an editor and add the following at the bottom
1 2 3 | export KEY='KEY FROM ENVIRONMENT' |
Zsh Shell
Open /.zprofile and add the following command at the bottom
1 2 3 | export KEY='KEY FROM ENVIRONMENT' |
Visual Studio
If you are debugging the code using the visual studio, remember that it also loads the environment variables from the launchSettings.json. The settings from the launchSettings.json always overwrite any environment variable we define in the OS.
A typical launchsetting.json is as below. We can add any environment variable under the node environmentVariables. for each debug profile.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 | { "iisSettings": { "windowsAuthentication": false, "anonymousAuthentication": true, "iisExpress": { "applicationUrl": "http://localhost:61764", "sslPort": 44369 } }, "profiles": { "IIS Express": { "commandName": "IISExpress", "launchBrowser": true, "environmentVariables": { "ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development", "KEY" : "Key from LaunchSettings.json" } }, "EnvironmentVariable": { "commandName": "Project", "launchBrowser": true, "environmentVariables": { "ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development", "KEY" : "Key from LaunchSettings.json" }, "applicationUrl": "https://localhost:5001;http://localhost:5000" } } } |
You read more about launchSettings.json & debug Profile
Visual Studio, loads the environment variables when it starts up. Hence if you make any changes to the environment variable, your application will not read it. You have to restart the Visual Studio to reload the environment variables
Visual Studio Code
The visual studio uses the .vscode/launch.json file for configuration. The file is as shown below. You can change the environment variable from the "env" node.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 | { // Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes. // Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes. // For more information, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387 "version": "0.2.0", "configurations": [ { "name": ".NET Core Launch (web)", "type": "coreclr", "request": "launch", "preLaunchTask": "build", "program": "${workspaceFolder}/bin/Debug/netcoreapp3.1/vscode.dll", "args": [], "cwd": "${workspaceFolder}", "stopAtEntry": false, "serverReadyAction": { "action": "openExternally", "pattern": "\\bNow listening on:\\s+(https?://\\S+)" }, "env": { "ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development", "KEY" : "Key from launch.json" }, "sourceFileMap": { "/Views": "${workspaceFolder}/Views" } }, { "name": ".NET Core Attach", "type": "coreclr", "request": "attach", "processId": "${command:pickProcess}" } ] } |
dotnet run
dotnet run command runs the application from the source code. It will pickups the environment variables from the OS. But if you make any changes to the environment variable, ensure that you close and reopen the shell
You can use the --launch-profile flag to specify the debug profile. In such case, the environment variable from the launchSettings.json, will take precedence over those from the OS
1 2 3 | dotnet run --launch-profile="Test" |
IIS Server
For the IIS Server use the web.config file to set the value of any environment variables. Add the following under the aspNetCore node
Use web.config
1 2 3 4 5 | <environmentVariables> <environmentVariable name="KEY" value="Key from web.config" /> </environmentVariables> |
The sample web.config. is as shown below.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <configuration> <location path="." inheritInChildApplications="false"> <system.webServer> <handlers> <add name="aspNetCore" path="*" verb="*" modules="AspNetCoreModuleV2" resourceType="Unspecified" /> </handlers> <aspNetCore processPath="dotnet" arguments=".\EnvironmentVariable.dll" stdoutLogEnabled="false" stdoutLogFile=".\logs\stdout" hostingModel="inprocess" > <environmentVariables> <environmentVariable name="KEY" value="Key from web.config" /> </environmentVariables> </aspNetCore> </system.webServer> </location> </configuration> |
If you make changes to the web.config in the production server, you will lose the changes, when you publish again. Hence create a web.config file in the project root folder and update the environment variables. This way you will not loose the change.
Precedence
The default configuration loads the environment variable after appsettings.json, appsettings.Environment.json, & user secrets. Therefore, any settings we set in the environment variable is overrides values from the above sources
Hierarchical keys
You can set the Hierarchical keys by using the __ double underscore. You can also use double colon (:), but it may not support it.
1 2 3 | setx Logging__LogLevel__Default=Information |
We can read the configuration using the configuration service.
1 2 3 | _config.GetValue<string>("Logging:LogLevel:Default"); |
EnvironmentVariablesConfigurationProvider
EnvironmentVariablesConfigurationProvider is the Configuration Provider. It contains the extension method AddEnvironmentVariables which is responsible loading the Environment Variables.
AddEnvironmentVariables takes one optional parameter prefix. When specified the method will load only those variables, which begins with that prefix
For Example consider the following environment variables
1 2 3 4 5 | setx settings_option1=Value1 setx settings_option2=Value2 setx option3=Value3 |
The method AddEnvironmentVariables(prefix:"settings_"), will load only the first two variable. The prefix is stripped off when the configuration key-value pairs are read.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | public static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(string[] args) => Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args) .ConfigureAppConfiguration((hostingContext, config) => { config.AddEnvironmentVariables(prefix:"settings_"); }) .ConfigureWebHostDefaults(webBuilder => { webBuilder.UseStartup<Startup>(); }); |
Hosting Environment Variable
ASP.NET Core apps configure and launch a host. The host is responsible for starting the app and running it. It is created when the application starts.
The Host also needs to be configured. The ASP.NET core also uses the environment variables to configure the host. These environment variables are prefixed with ASPNETCORE_{configurationKey}. For Example ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT
These Hosting Configurations are loaded at the app startup and even before the default configurations are loaded.
Reference
Read More


