We use the Table Attribute or Table Name Attribute to specify the table name and schema to the Entity Framework.
Table Name Convention
The Default entity framework code first convention uses the pluralized form of an entity class name to create the database table.
Consider the following model.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | public class Customer { public int CustomerID { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } } //Add this in Context class public DbSet<Customer> Customer { get; set; } |
The above entity model creates the table with the name customers in Entity Framework as shown in the image above. Note that the table name is pluralized. You can override this behavior using the Table attribute. This attribute resides in System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema
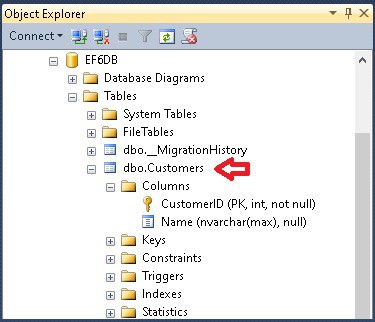
Table Attribute
Table attribute overrides the default entity framework code first convention, which creates the table with the name same as the class name. We apply the attribute to the class and not on the Property. The EF will create a table with the name specified in this attribute.
Syntax
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | Table(string name, Properties:[Schema = string]) Where Name: Sets the name of the table the class is mapped to. Schema: Sets the schema of the table the class is mapped to. |
Table Name
In the following example, we have updated our domain model Customer and applied the table attribute CustomerMaster
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | //Import required using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema; [Table("CustomerMaster")] public class Customer { public int CustomerID { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } } //Add this in Context class public DbSet<Customer> Customer { get; set; } |
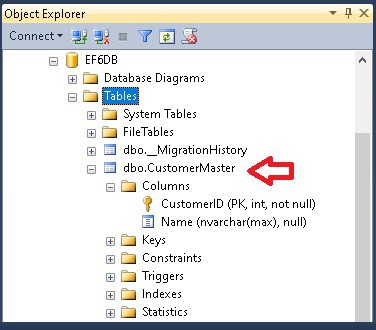
Table Schema
The above example created the table CustomerMaster under the schema dbo. You can also specify a table schema using the Schema attribute as shown below. The example below creates the CustomerMaster table with the schema “Admin”
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | //Import required using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema; [Table("CustomerMaster", Schema = "Admin")] public class Customer { public int CustomerID { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } } //Add this in Context class public DbSet<Customer> Customer { get; set; } |
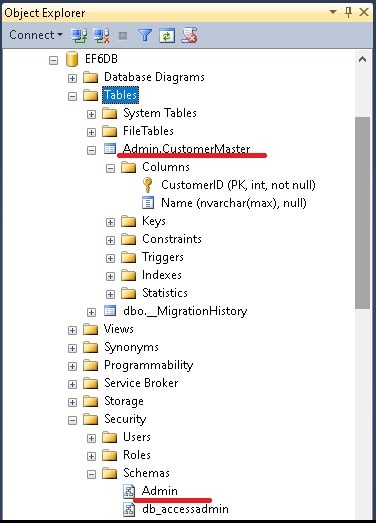
The dbo is now changed to Admin. If the schema does not exists, then EF will create one.