In the last tutorial, we looked at how to use Fluent API in entity framework Code First. In this tutorial let us look at the how to configure the Entity mappings using Fluent API
Create the C# Console project as specified in this Entity Framework Code First tutorial.
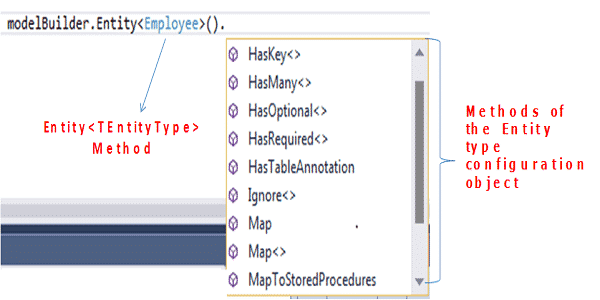
Entity Type Mapping
We are going to use the following domain class for this tutorial. The model has an Employee and Department class. It has an IgnoreThisTable class, which we do not want to include in the database. The ContactInfo is a Complextype class, which is referenced by both Employee and Department class.
Download the source code from github
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | public class Employee { public int EmployeeID { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public ContactInfo EmployeeContact { get; set; } } public class Department { public int DepartmentID { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public ContactInfo DepartmentContact { get; set; } } public class IgnoreThisTable { public int IgnoreThisTableID { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } } //This is a complex type public class ContactInfo { public string Email { get; set; } public string Phone { get; set; } } |
Table of Contents
Configuring the Entity Types
The configuration of the entity types is done using the generic method Entity<TEntityType> of the Dbmodelbuilder object. This method requires you to pass the entity type as the parameter. It returns the entitytypeconfiguration object which is then used to configure the entity. This class lives in assembly. System.Data.Entity.ModelConfiguration
Table Name
By Default Entity Framework uses the DbSet Property name to create the table Name. You can override this with the ToTable method of EntityTypeConfiguration object. The following code creates the mstEmployee Table for the employee Class
1 2 3 | modelBuilder.Entity<Employee>().ToTable("mstEmployee"); |
Table Schema
The “Totable” also has the second parameter, which takes the schema of the Table to be created. The example code is shown below creates the table with the schema admin instead of dbo.
1 2 3 | modelBuilder.Entity<Department>().ToTable( "mstDept","admin"); |
Primary Key
You can configure the Primary key using the HasKey method of entityTypeConfiguration as shown below.
1 2 3 | modelBuilder.Entity<Employee>().HasKey(e => e.EmployeeCode); |
Composite Primary Key
Composite Primary Key can be created using the HasKey method as shown below
1 2 3 | modelBuilder.Entity<Department>().HasKey(e => new { e.DeptCode, e.Name }); |
Ignore Property
Ignore method used to disable mapping of property to a column in the database. The Budget Property of Department table is not mapped to the database column in the following sample code
1 2 3 | modelBuilder.Entity<Department>().Ignore(t => t.Budget); |
Ignore table
Ignore method of the modelBuilder class will exclude the database mapping for the type selected. The following code will ensure that the IgnoreThisTable is not created in the database.
1 2 3 | modelBuilder.Ignore<IgnoreThisTable>(); |
Complex Type
Code First Convention detects a Complex type when it finds one. You can also specify the complextype in Fluent API using the ComplexType method as shown below.
1 2 3 | modelBuilder.ComplexType<ContactInfo>(); |
The Final DbContext Class for the above examples is as shown below.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 | public class EFContext : DbContext { public EFContext() : base("EFDatabase") { Database.SetInitializer<EFContext>(new DropCreateDatabaseAlways<EFContext>()); } protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder) { //Table Name modelBuilder.Entity<Employee>().ToTable("mstEmployee"); //Table Name with schema modelBuilder.Entity<Department>().ToTable( "mstDept","admin"); //Primary Key modelBuilder.Entity<Employee>().HasKey(e => e.EmployeeCode); //Composite Primary Key modelBuilder.Entity<Department>().HasKey(e => new { e.DeptCode, e.Name }); //Ignore the Property. Budget column is not created in the table modelBuilder.Entity<Department>().Ignore(t => t.Budget); //Ignore method disables the creation of table IgnoreThisTable modelBuilder.Ignore<IgnoreThisTable>(); //Complex Type Registration modelBuilder.ComplexType<ContactInfo>(); base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder); } public DbSet<Employee> Employees { get; set; } public DbSet<Department> Departments { get; set; } public DbSet<IgnoreThisTable> IgnoreThisTables { get; set; } } |
Program.cs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | static void Main(string[] args) { try { using (var ctx = new EFContext()) { ctx.Employees.Select(e => e.EmployeeID == 0); } } catch (Exception ex) { Console.WriteLine(ex.Message); } Console.WriteLine("Press any key to close"); Console.ReadKey(); } |