We are going to look at how to Configure Many to Many Relationship in Entity Framework in this tutorial. You can configure Many to Many Relationship either using Default Conventions, Data Annotations or Fluent API.
You can visit the Tutorial Relationships in Entity Framework to learn how to configure one-to-one or one-to-many relationships between entities.
Table of Contents
Configure Many-to-Many relationship
The relationship between employee and projects is many to many. The employee can be part of more than one project. The Projects can have many employees. The Many to Many Relationship usually involves the creation of a join table. The join table will have a composite primary key consisting combination of the primary key of both employees and project table.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | public class Employee { public int EmployeeID { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } //Navigational Property public virtual ICollection<Project> Projects { get; set; } } public class Project { public int ProjectID { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } //Navigational Property public virtual ICollection<Employee> Employees { get; set; } } |
Note that navigational property in both the classes returns the collection.
Many to Many Relationship in Code First Convention
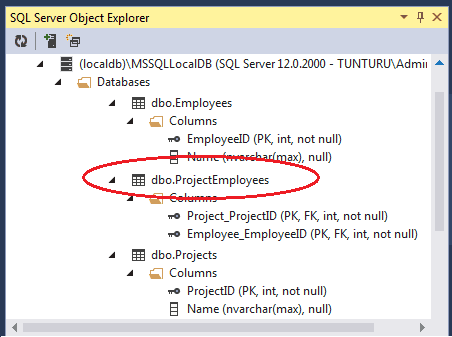
Code First Default Convention creates the join table to handle the Many-to-Many relationship. The above model results in the creation of Join table ProjectEmployees tables. The Join Table will have primary key of the both the table
Many to Many Relationship Using Data Annotations
The Many to Many Relationship Using Data Annotations requires you to create the Join Table in the model
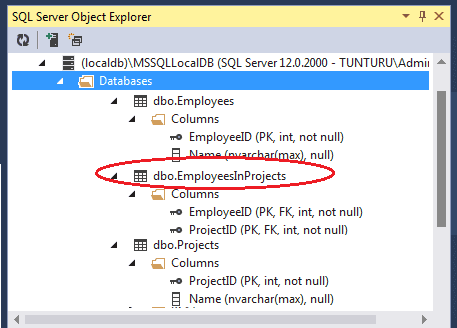
The Join Table EmployeesInProject will have properties for the primary key of the both the table. It will have two navigational properties one each for employee and Project class. The Employee and Project class will have the navigational property which maps to the Join Table EmployeesInProject.
The model is as shown below.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | public class Employee { public int EmployeeID { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public virtual ICollection<EmployeesInProject> EmployeesInProject { get; set; } } public class Project { public int ProjectID { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public virtual ICollection<EmployeesInProject> EmployeesInProject { get; set; } } public class EmployeesInProject { [Key] [Column(Order=1)] public int EmployeeID { get; set; } [Key] [Column(Order = 2)] public int ProjectID { get; set; } [ForeignKey("EmployeeID")] public Employee Employee { get; set; } [ForeignKey("ProjectID")] public Project Project { get; set; } } |
The above model is mapped to the following database schema as shown in the image below
Many to Many Relationship Using Fluent API
The Many to Many Relationship can be achieved using HasMany and WithMany methods.
1 2 3 4 5 | modelBuilder.Entity<Employee>() .HasMany(e => e.Projects) .WithMany(e => e.Employees); |
HasMany takes the navigational property of the employee table and sets up the Many Relationship in employees table and WithMany does the same on projects table. The Code first creates the join table employeeProjects which has primary keys from both the table.
Alternately you can define the code as follows. Only difference above and this code is that the Name of the Table generated here is ProjectEmployees.
1 2 3 4 5 | modelBuilder.Entity<Project>() .HasMany(e => e.Employees) .WithMany(e => e.Projects); |
You can change the name of the join table using the map method. The following code Creates the join table “EmployeesInProject” and also creates the Column EmployeeID and ProjectID. The Generated Schema is exactly the same as the one which was created using the data annotations.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | modelBuilder.Entity<Employee>() .HasMany(e => e.Projects) .WithMany(e => e.Employees) .Map(m => { m.ToTable("EmployeesInProject"); m.MapLeftKey("EmployeeID"); m.MapRightKey("ProjectID"); } ); |
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we looked at How to create Many to Many Relationship in Entity Framework using Default Convention, Data Annotations, and Fluent API


After implementing many-to-many relationship using data annotations, do I need to declare the DbSet in the context?
Yes
declare the DbSet of all domain classes.