We are going to look at how to Configure One to Many relationships in entity framework in this tutorial. One to Many Relationships can be configured using Default Conventions, Data Annotations or Fluent API.
Table of Contents
One to Many relationships in Entity Framework
Let us take an example of the relationship between the employee and the department to which employee belongs to. The relationship between employee and the department is One to Many. The employee belongs to only one department. The department can have many employees. In a One to Many relationship Primary key of the department table (DepartmentID) is defined as Foreign key in the Employees table
Our Model
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | public class Employee { public int EmployeeID { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } //Navigational Property public virtual Department Department { get; set; } } public class Department { public int DepartmentID { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } //Navigational Property public virtual ICollection<Employee> Employees { get; set; } } |
Note that navigational property in the employee class returns the reference to the department object. The navigational property in Department class returns the employees collection.
One to many relationship Using Default Convention
Code first default convention uses the navigational property to determine which class is dependent on which. The above model mapped to the database as shown in the image below
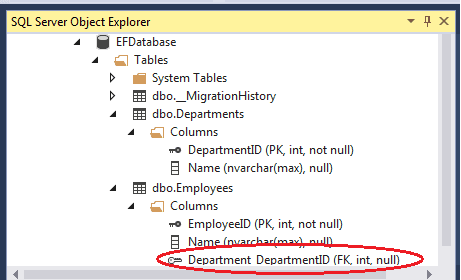
Note the Department_DepartmentID is added to the employee table by the Code First. This field is marked as Foreign Key. Also Note that Department_DepartmentID is created as Nullable Column
Foreign key Property
The above model created the Foreign Key Department_DepartmentID in the employee Table. You can include the foreign Key Property in the dependent class (Employee). The Code First will not create the Foreign key column, but uses the existing property.
For Example add the DepartmentID Property to the Employee class. The Code First will mark the DepartmentID as the foreign key and will not add the Department_DepartmentID as in the previous case
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | public class Employee { public int EmployeeID { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public int DepartmentID { get;set;} public virtual Department Department { get; set; } } public class Department { public int DepartmentID { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public virtual ICollection<Employee> Employees { get; set; } } |
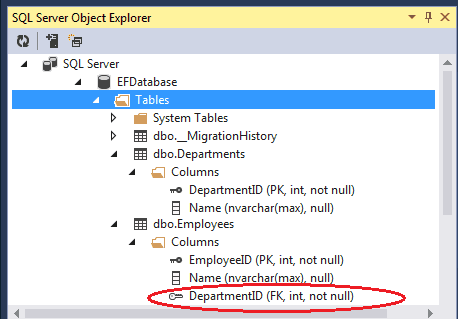
Note that the DepartmentID is created as Not Nullable column. If you want Nullable DepartmentID column, then define the property as Nullable as shown in the code below
1 2 3 | public int? DepartmentID { get;set;} |
One to many Relationship Using Data Annotations
The default convention makes an excellent work inferring the model and creates the necessary relationships. But the default conventions work only if you follow the conventions correctly. For Example in the previous example, if you add DeptID instead of DepartmentID then the Code first fails to detect the relationship
This can be overridden by using the Data annotations ForeignKey attribute on the navigational property as shown below.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | public class Employee { public int EmployeeID { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } [ForeignKey("Dept")] public int DeptID { get;set;} public virtual Department Dept { get; set; } } public class Department { public int DepartmentID { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public virtual ICollection<Employee> Employees { get; set; } } |
Here DeptID is created as Not Nullable Column.
You can refer to the ForeignKey Dataannotation Attribute for more information on ForeinKey Attribute.
One to many Rrelationship Using Fluent API
One to many relationships using Fluent API is done using the HasRequired and WithMany methods of the entityTypeConfiguration object as shown below
1 2 3 4 5 | modelBuilder.Entity<Employee>() .HasRequired(e => e.Department) .WithMany(d => d.Employees); |
We have used HasRequired on employee entity and takes the navigational property Department to set up the relationship on the employee table. HasRequired method returns the RequiredNavigationPropertyConfiguration. The Inverse relationship, then can be specified using the WithMany method. WithMany takes the navigational property Employees from the entity Department. WithMany method is used to set up the Many side of the relationship
The above code will create a Foreign Key Column Department_DepartmentID in employee Table. The Database is as shown in the 1st Image. Since we used HasRequired the Foreign key is Not Null
To Create a Nullable Foreignkey we can use HasOptional method instead of HasRequired as shown below
1 2 3 4 5 6 | //Nullable Department_DepartmentID in employee table modelBuilder.Entity<Employee>() .HasOptional(e => e.Department) .WithMany(d => d.Employees); |
Above examples creates Department_DepartmentID column in the database table.
You can use the HasForeignKey method to create DeptID as Foreign Key. This will create DeptID as Not Nullable column
1 2 3 4 5 6 | modelBuilder.Entity<Employee>() .HasRequired(e => e.Dept) .WithMany(d => d.Employees) .HasForeignKey(e => e.DeptID); |
To Create a Nullable Foreign Key use the Fluent API method IsOptional as shown below
1 2 3 4 5 | modelBuilder.Entity<Employee>() .Property(e => e.DeptID) .IsOptional(); |
1 2 3 4 5 6 | modelBuilder.Entity<Employee>() .HasOptional(e => e.Dept) .WithMany(d => d.Employees) .HasForeignKey( e => e.DeptID); |
Conclusion
The above sets up the One to Many Relationship using Data annotations & Fluent API. In the next tutorial let us look at how to Configure the Many to Many Relationship