We are going to look at how to Configure one to one relationship in entity framework. One to One Relationship can be configured using Data Annotations or Fluent API.
Table of Contents
One to One relationship in Entity Framework
Let us take the example of an Employee and Employee Address domain models and create a One to One relationship between them. In a One to one relationship PrimaryKey of Primary table (employeeID of employee table) is both Primary key and Foreign key in the dependent table (EmployeeAddress).
Basic Model
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | public class Employee { public int EmployeeID { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } // //Navigation property Returns the Employee Address public virtual EmployeeAddress EmployeeAddress { get; set; } } public class EmployeeAddress { public int EmployeeID { get; set; } public string Address { get; set; } // //Navigation property Returns the Employee object public virtual Employee Employee { get; set; } } |
Note that the we have created the navigational property which returns the reference to the related entity. In Employee class navigational property returns the reference to the EmployeeAddress object. In EmployeeAddress class navigational property returns the reference to the Employee object.
One to One Relationship using Default Convention
Navigational property in both the classes returns the object. This makes it difficult for Entity framework, to determine which class is dependent on which. Hence Setting up the One to One Relationship using default convention is not possible
One to One Relationship using Data Annotations
One to one relationship using data annotations is done using ForeignKey attribute on the dependent class. Remember that in One-to-One relationship, Primary key of the Primary table is both primary key and foreign key of the dependent table. Hence we use Key & ForeignKey Data Annotation attribute on employeeID property in EmployeeAddress class (Dependent). Our EmployeeAddress class will look like this
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | public class EmployeeAddress { [Key, ForeignKey(“Employee”)] public int EmployeeID { get; set; } public string Address { get; set; } // //Navigation property Returns the Employee object public virtual Employee Employee { get; set; } } |
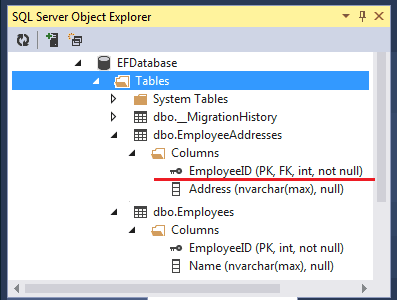
No Change is required in the Employee class. The Model is mapped to the database as shown in the image below
One to One Relationship using Fluent API
In Fluent API HasKey is used to configure the EmployeeID as Primary Key in the EmployeeAddress Table.
The next step is to create the one to one relationship using HasOptional method.. HasOptional takes the navigational property ( EmployeeAddress ) and sets up the relationship on employee table. This relation is optional, which means that the you can save employee data without employeeAddress.
HasOptional returns the OptionalNavigationPropertyConfiguration, which we can use to set up the inverse relationship (relationship on employeeAddress). Here WithRequired which takes the navigation property Employee ( from the table employeeAddress) and sets the relationship on the second table. WithRequired specifies that, the you cannot save the employeeAddress without corresponding employee Records.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | modelBuilder.Entity<EmployeeAddress>() .HasKey(e => e.EmployeeID); modelBuilder.Entity<Employee>() .HasOptional(e => e.EmployeeAddress) .WithRequired(a => a.Employee); |
Conclusion
The above sets up the One to One Relationship using Data annotations & Fluent API. In the next tutorial let us look at how to Configure the One to Many Relationship


do you know de way