In this tutorial, learn how to work with different languages in SQL Server. Learn how to change SQL server language settings. Find out the language list that SQL server supports along with the language codes & language id etc. We also lean how to change the language settings in case of contained database.
Table of Contents
Finding the Current Language
@@LANGUAGE global variable returns the name of the language that sql server uses currently.
1 2 3 | select @@language; |
Finding the language List
To find the list of languages that SQL Server supports run sp_helplanguage stored procedure without any parameter
It will list the langid (language id), name (language name) etc.
1 2 3 | exec sp_helplanguage |
Language Settings in SQL Server
How you set the language of a database depends on whether it is a contained database or not.
A contained database is a database that is isolated from other databases and from the instance of SQL Server that hosts the database. This SQL Server introduced this feature since version 2012.
If the database is not contained then the settings needs to change at instance level and at login account.
In case of contained database, you need to set it for the database & database user account.
We look at the both the scenarios.
Setting Language for SQL Server / Instance
In SQL Server language can be set at three places.
- Instance
- User Login Account
- Current Session
SQL Server always uses the language set in the current session. If it not set then it uses the default language from the users login account.
The Instance Level language settings are used as the default language when we create a new login account.
Instance Level Language Settings
The SQL Server picks up the language settings from the OS at the time of installation We can change this later either using the
- SQL Server Enterprise Manager
- TSQL Query
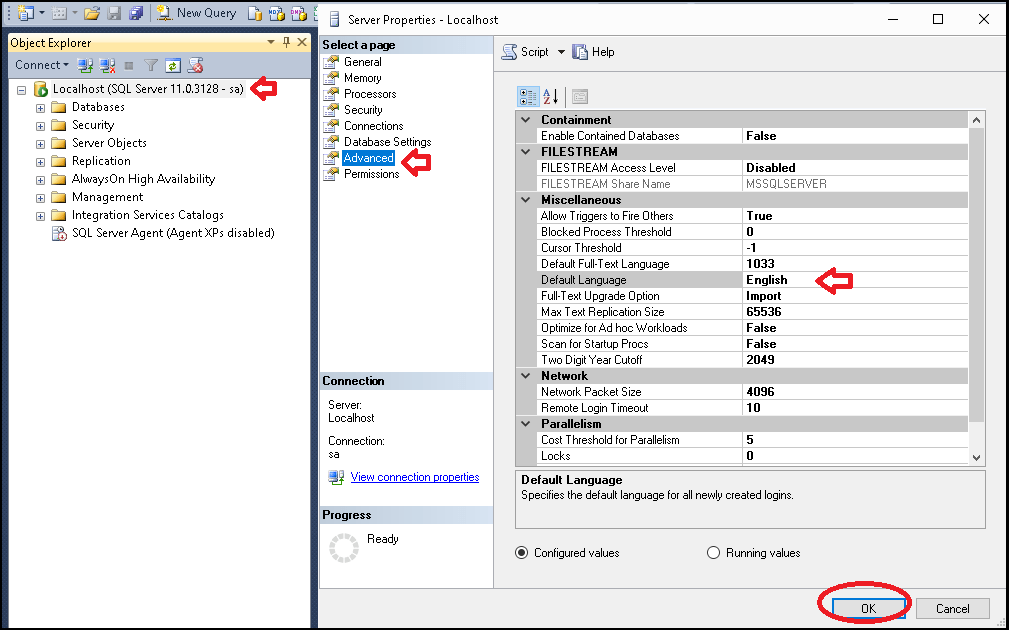
Change Default Language Using SSMS
- In Object Explorer, right-click on the server instance and select Properties.
- Click the Advanced Tab
- Choose the language from the Default language drop down.
- Click on Save
Change Default Language Using Query
- Run
exec sp_helplanguageto view the list of languages - Note down the language id of the language you want to set.
- Run the
sp_configureas shown below
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | EXEC sp_configure 'default language', 2 ; GO RECONFIGURE ; GO //result Configuration option 'default language' changed from 0 to 2. Run the RECONFIGURE statement to install. |
Note that changing the settings at instance level will not affect the already existing login account. But it will make the new language as default for the new login accounts.
Setting Language Settings for Login account
To change the language of an existing login you can either use the GUI Tools in SSMS or execute a ALTER LOGIN query.
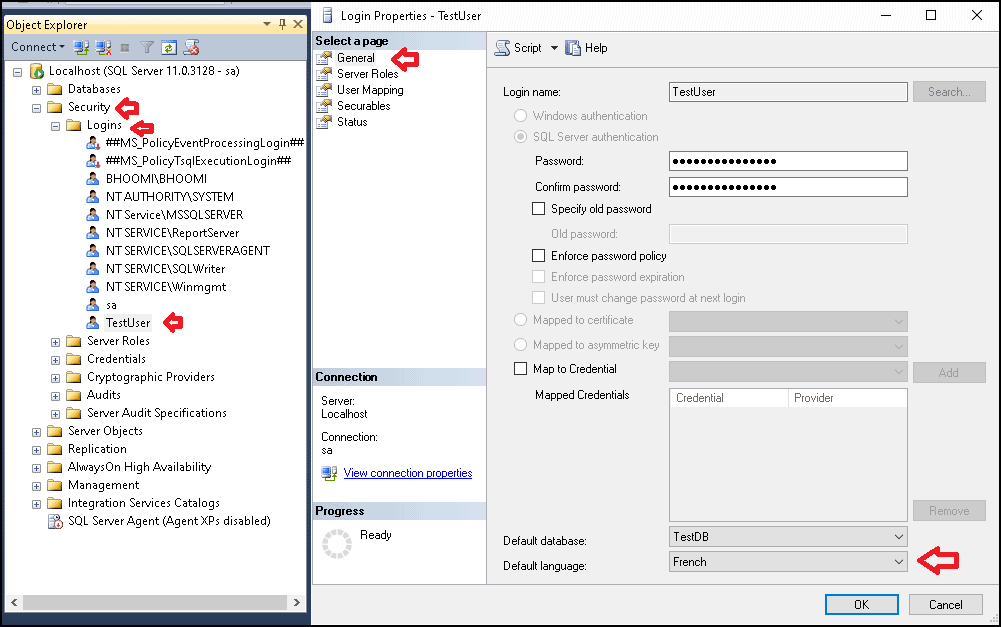
Using SSMS
- Open the SSMS
- Select the User under the Security-> Login option
- Right click on click on properties
- Under the General tab choose the desired language from Default Language from the drop down.
- Click on Ok to save
Using Query
You can use the Alter User Query to change
1 2 3 | ALTER LOGIN [TestUser] WITH DEFAULT_LANGUAGE=[german] |
Setting Language for Contained Database
The SQL Server since version 2012 has the option of creating contained database. In case of contained database the language is set at
- Database level
- Contained User Level
- Session
Setting Language at Database Level
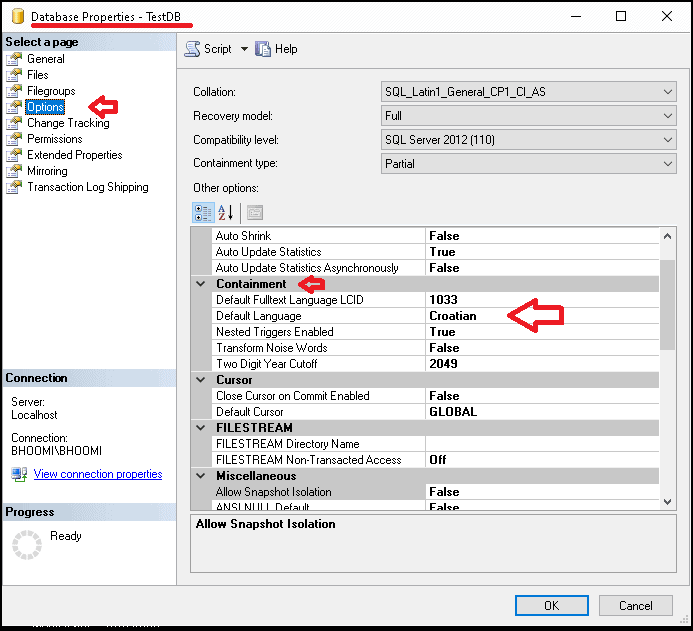
Using SSMS
- In Object Explorer, right-click on the database and select Properties.
- Click the Options Tab
- Choose the language from the Default language drop down under the section containment. You will see this option only in case of contained database.
- Click on Save
Using Query
- Run
exec sp_helplanguageto view the list of languages - Note down the language id, lcid or language name of the language you want to set.
- Run the
ALTER DATABASEas shown below with either language id, lcid or language name
1 2 3 | ALTER DATABASE [TestDB] SET DEFAULT_LANGUAGE = 1050 |
Setting Language of the User
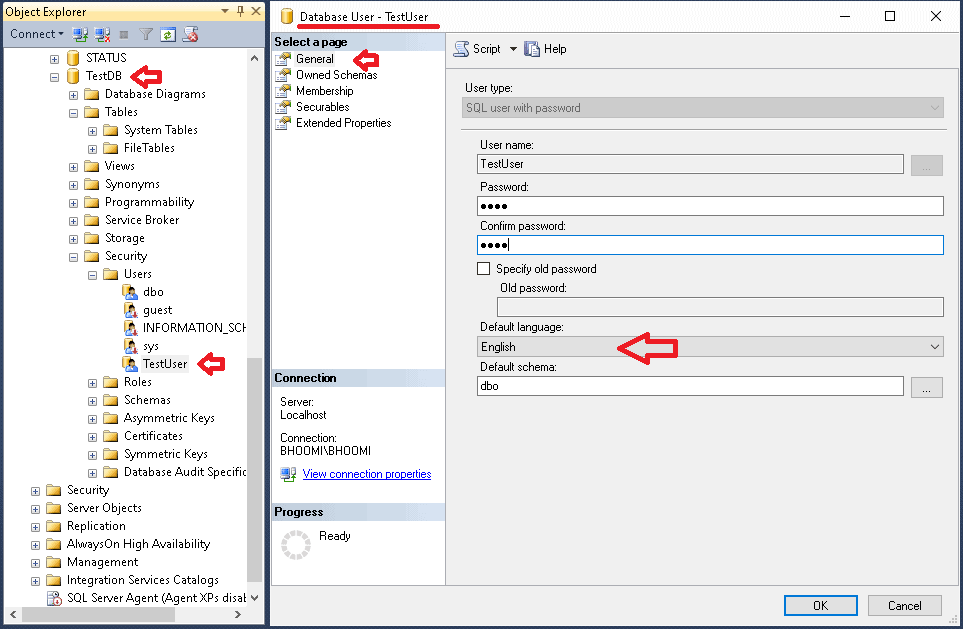
Using SSMS
- In Object Explorer, under the
database -> Security -> Users, select the users. - Click the General Tab
- Choose the language from the Default language drop down. This option is only if the database is a contained database.
- Click on Save
Using Query
Run the ALTER USER as shown below with either language id, lcid or language name
1 2 3 | ALTER USER [TestUser] WITH DEFAULT_LANGUAGE=[English] |
Session Level Language Settings
Changing the session level language is same for both contained and non contained scenarios. Use the SET LANGUAGE TSQL Command to change the language of the current session.
1 2 3 | SET LANGUAGE { [ N ] 'language' | @language_var } |
1 2 3 4 | SET LANGUAGE 'French' select @@language; |
This will only effect the current session.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | SET LANGUAGE 'French' select @@language; //Français Declare @dt date set @dt='2016-12-01' select format( @dt,'d') //01/12/2016 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | SET LANGUAGE 'English' select @@language; //us_english Declare @dt date set @dt='2016-12-01' select format( @dt,'d') //12/1/2016 |
The SET LANGUAGE also uses the SET DATEFORMAT to set the date format


Thank you!.
I was looking why changing the database language didn’t work, it was the login account!